Portrait of David B. Runnells taken by Life Magazine in 1950
Portrait of David B. Runnells taken by Life Magazine in 1950David Benton Runnells, Architect 1913-1973
Architect, David B. Runnells traveled extensively in Europe after graduating from the University of Illinois. He was heavily influenced by the work of Alvar Aalto while traveling through, Finland and Sweden on a scholarship to the University of Stockholm.
Runnells was a student of Eliel and Eero Saarinen, studying city planning at Cranbrook, a hotbed of modern design education. Other students attending at that time were Charles and Ray Eames, Florence Knoll, Harry Bertoia, Benjamin Baldwin, Harry Weese and Jack Lenor Larsen. Runnells worked in the Saarinen offices during part of World War II and did competitions with co-worker and Case Study House Architect, Ralph Rapson.
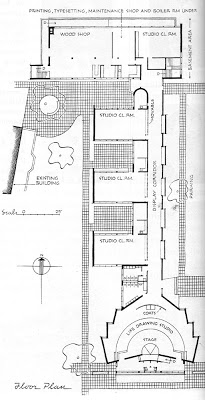
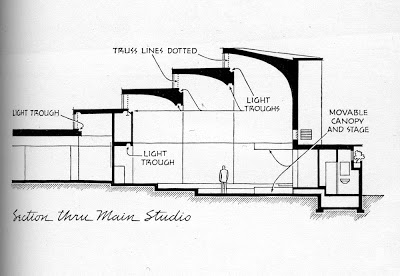
Runnells eventually settled in Kansas City sometime around 1941 as head of the industrial design department of the Kansas City Art Institute. He was a director of planning with the Kansas City Planning Department from 1943-46. He became an architect in 1946 and partnered in Runnells Clark Waugh and Matsumoto Architects. Together, they did one of his best known projects, the new Art School building for the Kansas City Art Institute. The only other project known to have come from that partnership is the James I. Clark Residence.
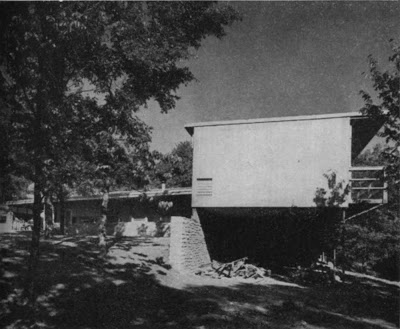
After the partnership dissolved, with Waugh and Matsumoto leaving to teach, Runnells went on to do merchant home builder designs and custom homes, many of which were built by modern builder, Don Drummond. The Revere Homes are his best known merchant builder design. The Reed Residence is the best surviving example of his large custom residential work. The two custom personal residences that he designed for himself and for Don Drummond have both been demolished. His 1966 design for the Alpha Kappa Lambda Fraternity in Lawrence, Kansas has also been demolished.





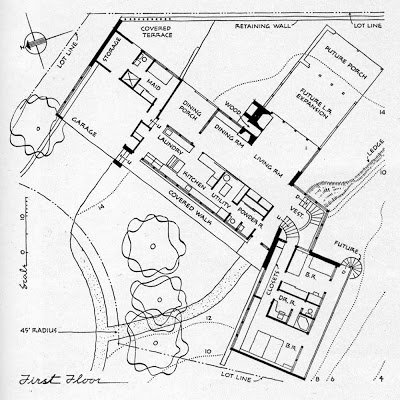
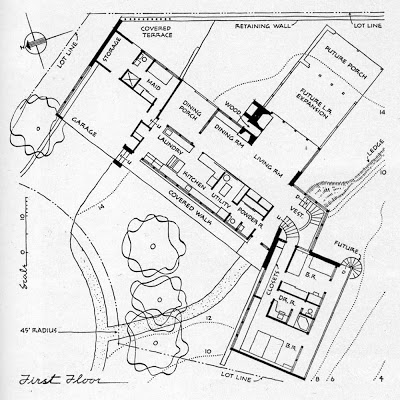
 bedroom wing, additional bedrooms to be added later at lower level
bedroom wing, additional bedrooms to be added later at lower level




 wall between dining area and kitchen
wall between dining area and kitchen